Wood Topics, Projects and Issues
During a recent trip to Bruges, Belgium I got to do an unexpected timber assessment of the belfry of Bruges (visual grading, checks, splits and even some powder post beetles.)
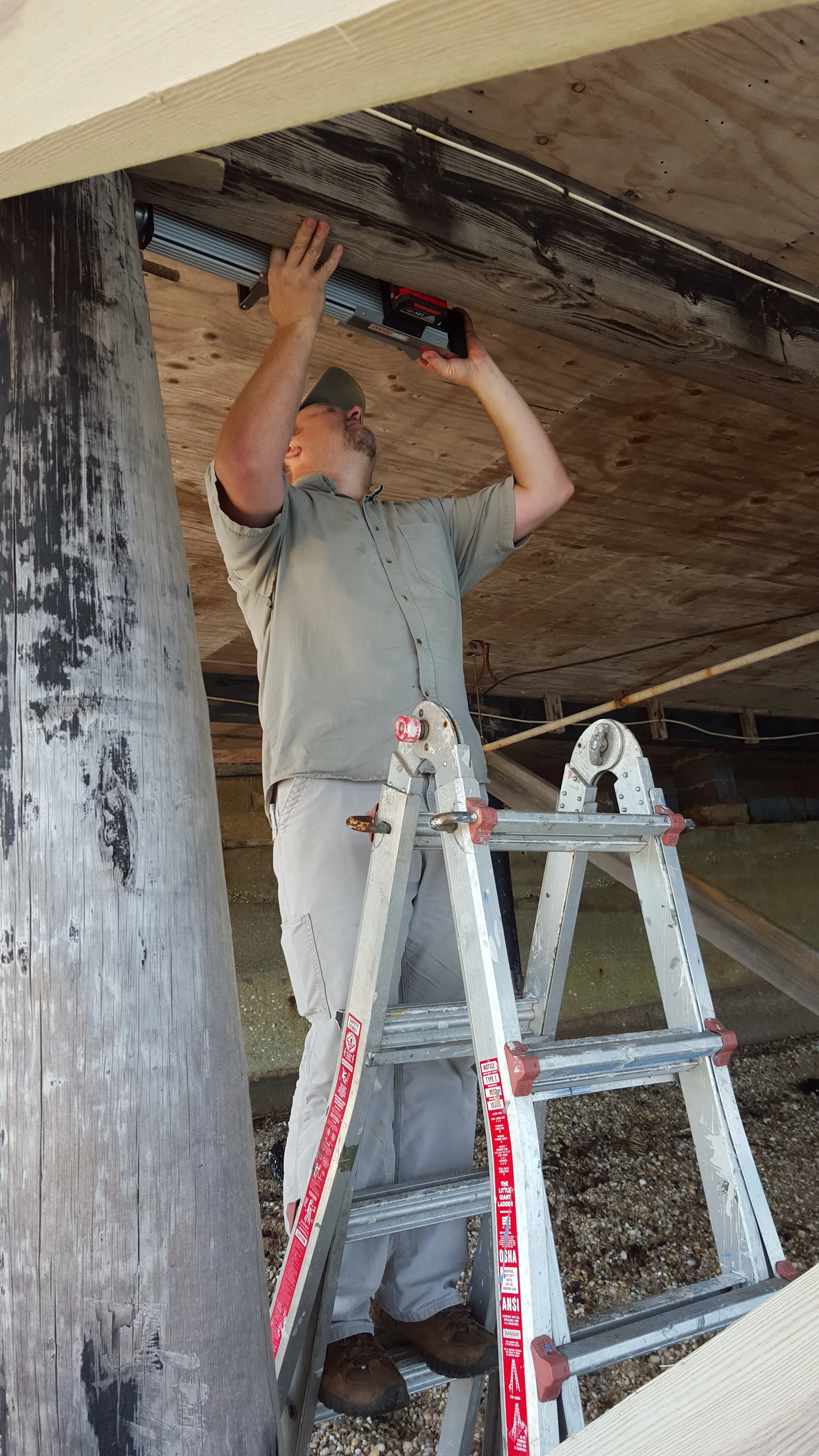
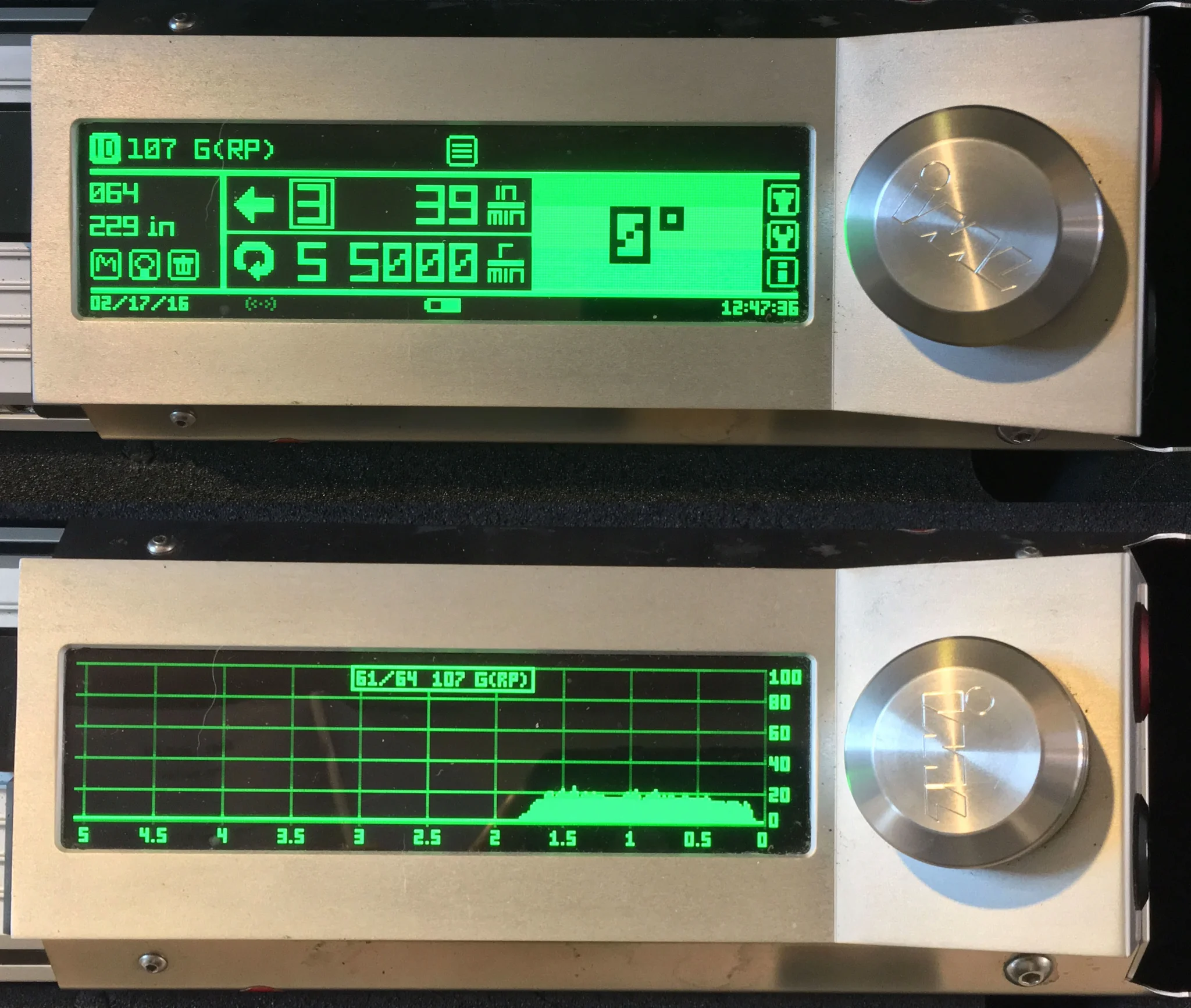
Damage from wood boring insects, such as termites, can go undetected for long periods of time resulting in extensive damage to wood frame structures. Additionally, wood decay can also go undetected for long periods of time. For this project the Resistograph was used as a non-destructive tool to document powder post beetle damage in a historic home, but instead extensive termite and wood decay damage was detected that was initially hidden.
Depending on the severity of a fire and the damage to the timbers, there may be an opportunity to salvage the materials and reuse them. For this project a Resistograph was utilized to determine char depths as part of the scope of work required to determine effective cross sections and allowable properties for several timbers that were reclaimed after a fire broke out in three historical structures.
Checks and splits are common in wooden timbers and dimension lumber. In most instances they are acceptable under the current grading rules for timbers and lumber, except in certain circumstances.
Wood Pathology as it pertains to structures, such as older or historical buildings, is the process of assessing the condition of the elements in the structure using several methods. A wood pathologist should be able to determine allowable properties, determine wood species, assess wood decay and other biological deterioration, assess mechanical damage, perform non-destructive testing and any necessary chemical analyses so that a comprehensive condition assessment can be determined.
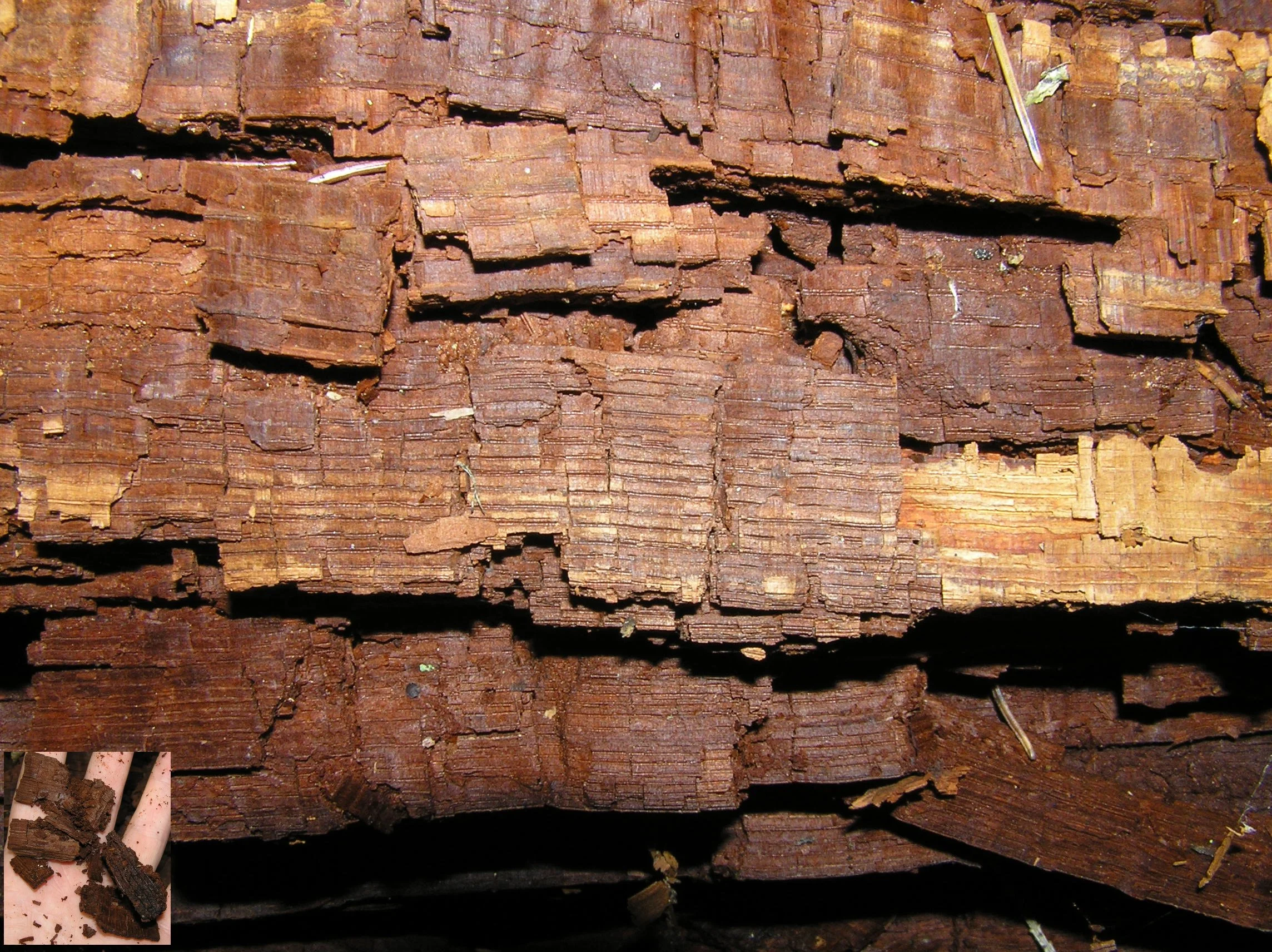
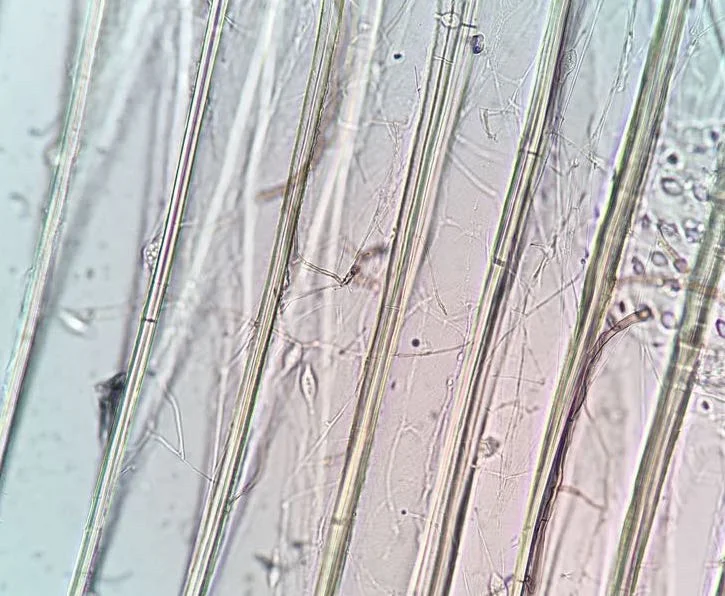
The effects of wood decay on strength loss are well documented in the wood science community. The most critical stages of wood decay are the incipient and early stages. In structures, an effective procedure commonly used to evaluate wood elements is the collection of increment cores which are then examined microscopically to document the presence or absence of wood decay.
Non destructive testing with a Resistograph is a very effective method for evaluating wood elements in structures, however, to verify the location of sound wood for engineering repairs it is critical to identify where wood decay is not present in the element(s) being tested. For this reason, microbiological analyses are often performed to supplement Resistograph testing data.
Summary of the practices and procedures for determining the reference design values and properties of lumber and timber elements in existing structures.
Summary of the issues associated with bowstring trusses.
General discussion of wood decay growth conditions, the effects of wood decay on the strength of wood, and wood decay in structures. Also discussed is how to optimize growth conditions for the cultivation of edible mushrooms using logs.
General description of soft rot wood decay and its association to a recent archaeological discovery.
Resistograph testing, or resistance drilling, of timbers in structures, utility poles, pilings and trees is a useful non-destructive testing tool. An understanding of wood and its structure are required for interpretation of the results. Used properly, the Resistograph is an effective non-destructive testing drill.